Planning the Environment
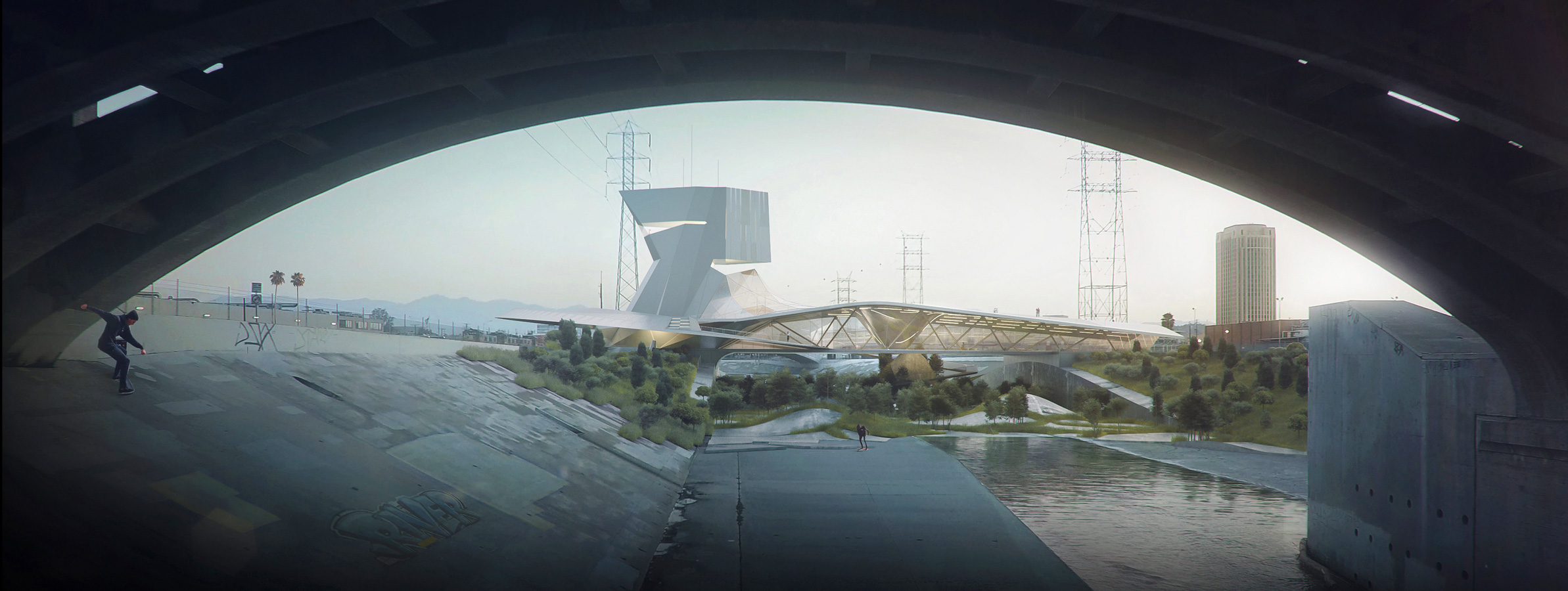
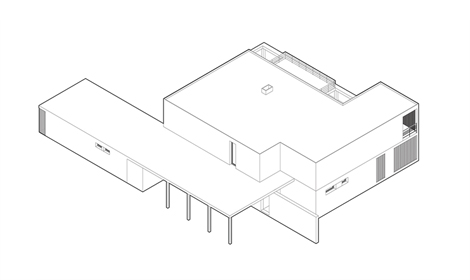
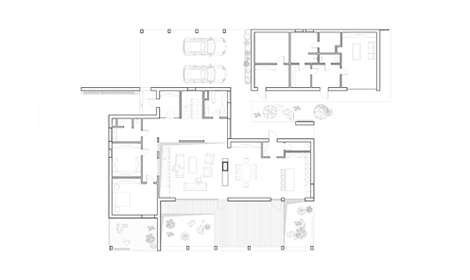
Architectural planning involves not only the internal spatial layout but also the structure’s harmony with its environmental and technical context. The architect increases livability by balancing elements such as heat, cold, light, air, moisture, and dryness—while also foreseeing natural risks like fire, earthquakes, floods, and other hazards.
Orientation
This process includes not only engineering solutions but also architectural expression. The building’s position, orientation, floor plan, and relationship with its surroundings become key instruments in design. In this sense, planning is not just an arrangement—it becomes a bearer of architectural identity.